NASA, alongside private industry partners, has taken a significant step in space exploration by enabling private spacecraft to land on the Moon, reshaping future lunar missions.
Key Highlights:
- US Lunar Return After 50 Years:
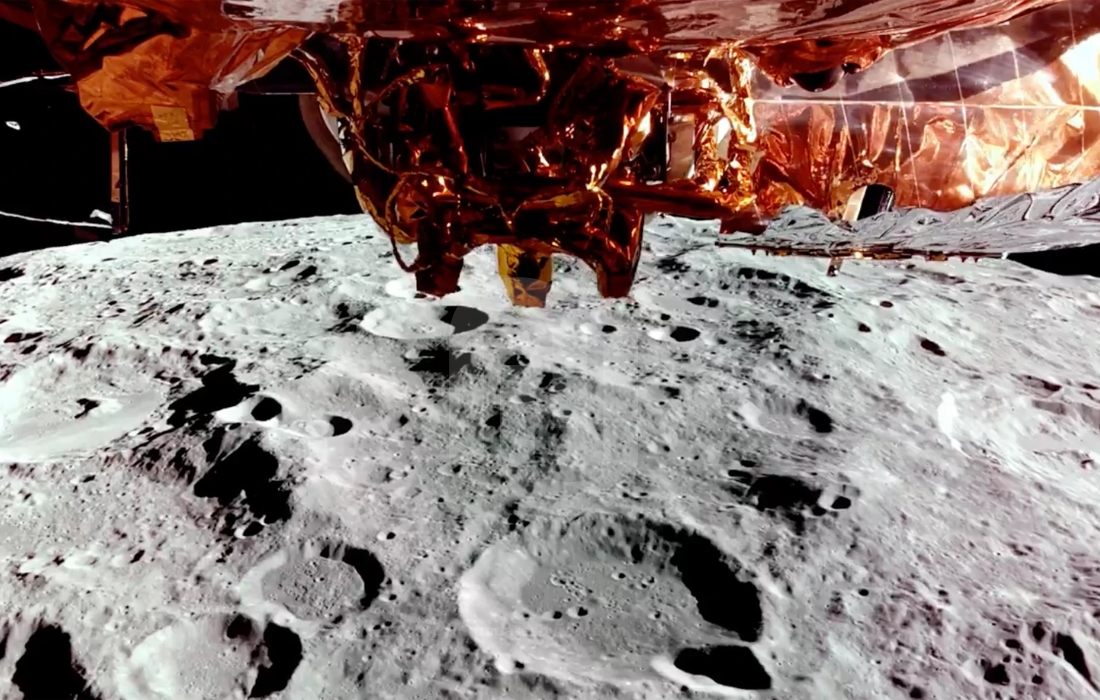
The US returned to the Moon in February, over five decades after the Apollo mission, with its first-ever private spacecraft landing. - Upcoming Missions:
Two more private spacecraft landings are scheduled within a week, reflecting NASA’s vision of making lunar missions routine. - Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission:
Blue Ghost, targeting Mons Latreille on the Moon’s northeastern side, carries advanced instruments for soil analysis, radiation testing, and GPS-based navigation. - Intuitive Machines’ IM-2 Mission:
Following its earlier success, Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander aims to explore the Moon’s southernmost region, equipped with rovers and a groundbreaking hopping drone named “Grace.” - NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS):
The $2.6 billion CLPS program supports private companies in delivering hardware to the Moon at reduced costs, paving the way for frequent lunar missions.
NASA’s collaboration with private companies marks a pivotal shift in space exploration, potentially influencing future missions to Mars.